think tank launches Elix: An all-in-one Business & Project Management Suite

Tunis, 15 May 2025 – think tank, a leading player in digital transformation across Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, officially announces the launch of Elix, a modular software suite designed to revolutionize the management of businesses, projects, processes, and teams—both in the private sector and in public institutions.
Yassine Kaaniche, General Manger think tank: „With Elix, we set out to build a living platform—one that grows with our clients. It’s more than just software; it’s a smart, open architecture designed to support business growth while ensuring performance, security, and adaptability.“
Designed for both private and public sectors
An intuitive platform, For every business need
Designed to meet diverse business needs, Elix offers a comprehensive suite of powerful, complementary modules, including a low-code editor for generating business objects, workflows & APIs, ticketing & tasks, Agile project management, test automation & release management, HR & administration tools, IT & inventory management, and much more. With its integrated AI assistant and mobile app, Elix automates routine tasks and keeps you in control of your work—anytime, anywhere.
Empowering every team
- Reduced software spending by eliminating redundant tools and optimizing budget allocation;
- Up to 30% increase in productivity through task automation and better resource management;
- Time savings on administrative tasks with automated workflows and an integrated AI Assistant;
- Faster, smarter decision-making, powered by real-time dashboards and consolidated insights & data;
- Stronger collaboration between departments, HR, IT, and project teams in a unified and agile work environment.
About think tank
Marketing & Communications Team
Sarah Cherif
sarah.cherif@thinktank-tunisie.com
Dorothee Schwarz
+49 (0)89 552677-0
For more information about Elix
Oracle APEX and the Future of
Low-Code Development

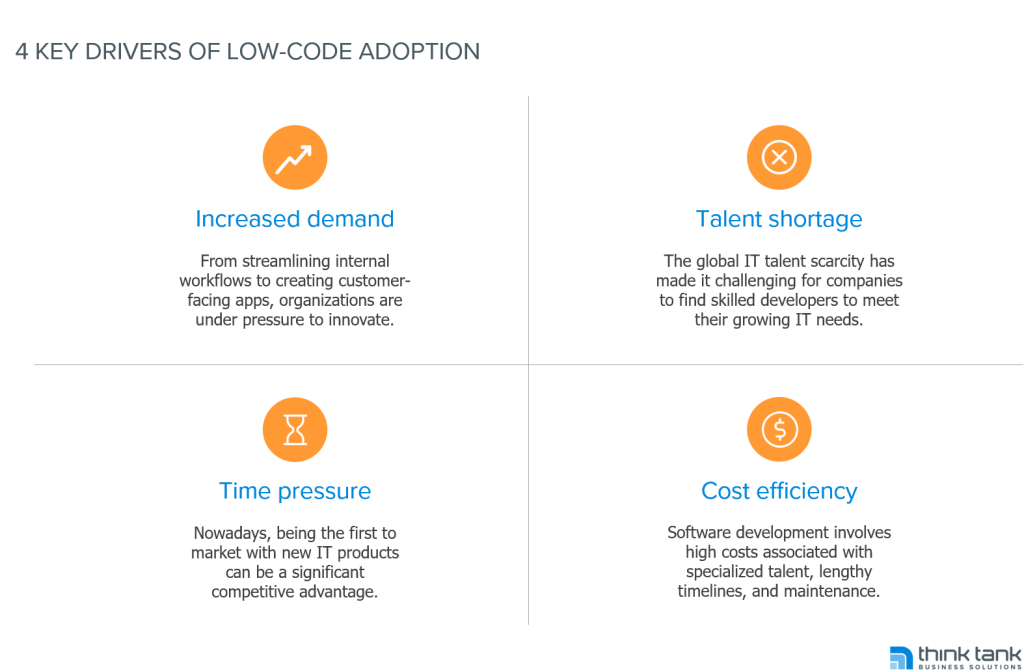
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses face constant pressure to innovate and deliver software solutions faster, more efficiently, and at lower costs. Low-code platforms have emerged as a pivotal force in this transformation, offering a means to accelerate application development while reducing the dependency on specialized programming skills.
Oracle APEX, a long-standing player in the low-code arena, is uniquely positioned to thrive amidst emerging trends in low-code development.
Four Low-Code Development Trends to watch
The adoption of low-code platforms has been nothing short of transformative for organizations of all sizes, from different industries. Low-code empowers business users with minimal coding experience to build applications, while also enhancing productivity for professional developers.
Trend #1 : AI & Automation Integration
- Code suggestions: AI-driven tools will provide real-time recommendations to optimize code snippets or suggest prebuilt templates.
- Workflow automation: Machine learning models will analyze data patterns to automate routine workflows and streamline processes.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Users will describe desired functionalities in natural language, and AI will translate this into functional application components.
Trend #2 : Interoperability and Ecosystem expansion
Low-code platforms will increasingly focus on seamless integration with external tools, databases, and cloud services. Cross-platform compatibility and extended plugin ecosystems will allow organizations to customize their low-code solutions further.
- Extended plugin ecosystems to enhance functionality and customization, low-code platforms will offer an expanded marketplace of plugins and connectors. These plugins will provide ready-made solutions to integrate with third-party tools (e.g., CRM systems, ERP software, data analytics platforms) and external databases.
- API-first approach adopted by low-code platforms, including support for RESTful APIs, GraphQL, and other industry-standard protocols to ensure smooth data flow between systems.
Trend #3 : Emphasis on Governance and Security
Trend #4 : Enhanced Collaboration Tools
As low-code platforms are increasingly adopted by both technical and non-technical users, the need for collaboration among various stakeholders will be more important than ever. Developers, business users, and designers must be able to work together seamlessly to accelerate agile development.
- Cross-functional dashboards: Low-code platforms will provide centralized dashboards that offer an overview of project progress, including real-time analytics, metrics, and performance insights per business unit.
- Design and prototyping tools: Designers and developers will have access to prototyping and wireframing tools within the low-code platform, allowing them to quickly visualize app designs, user interfaces, and workflows.
84% of businesses are adopting low-code or no-code tools to fill the technical gap left by the shortage of developers.
Source: Forrester
How Oracle APEX Fits into the Future of Low-Code
Oracle APEX is a low-code platform that enables businesses to build enterprise-grade apps significantly faster than traditional hand coding using popular JavaScript frameworks.
1. AI-powered Development
Oracle APEX integrates with Oracle’s AI and machine learning services, providing users with capabilities such as predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and AI-driven recommendations for application development. As AI becomes more embedded in Oracle’s cloud ecosystem, APEX users will have a seamless way to incorporate AI into their low-code applications.
2. Seamless Cloud Integration
With Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), APEX users already benefit from a highly integrated ecosystem. Upcoming trends like multi-cloud strategies and hybrid cloud architectures will see APEX serving as a bridge, enabling smooth connectivity between Oracle Cloud and other cloud providers.
3. Governance and Security
4. Collaboration and Low-Code Democratization
think tank: Pioneering Low-Code Solutions with Oracle Expertise
The future of low-code is undeniably bright, characterized by increased AI integration, greater automation, and enhanced collaboration. Oracle APEX, with its robust database foundation, enterprise-grade capabilities, and integration with Oracle’s AI and cloud ecosystem, is well-positioned to remain a leader in the low-code revolution.
At think tank, we have consistently leveraged low-code platforms like Oracle APEX to deliver innovative, scalable, and secure applications tailored to our clients’ needs, operating in both private and public sectors. Our expertise spans:
- Custom Application Development: Building enterprise-grade solutions with Oracle APEX, streamlining operations and driving digital transformation.
- AI & Automation Integration: Implementing Oracle’s AI and internal tools to enhance the functionality and intelligence of low-code applications.
- Seamless Cloud Deployments: Helping organizations optimize their Oracle Cloud Infrastructure with integrated low-code applications.
Ready to transform your organization with Low-Code?
From AI-driven applications to seamless cloud deployments, we’ll guide your low-code journey every step of the way.
Content:
Introducing Elix – All you need for Business & Project Management

In today’s fast-paced environment, agility and efficiency are key to success. Elix offers an all-in-one suite of business management tools and micro-apps helping organizations streamline their daily workflows and operations, cut costs, and boost productivity across different teams and departments.
Addressing today’s Business Challenges
Organizations, businesses, and modern workplaces are overwhelmed by too many apps (Project & task management, HR, Finance, document management, etc.) leading to operational inefficiencies, data loss, and high costs.
Lack of Monitoring
Managers find it more difficult to gain 360° visibility on overall operations, performance, and projects progress.
Fragmented Documents
Dispersed data and documents across various apps increases the error aof errors, data loss, and inconsistencies.
Financial Burden
Each tool comes with its costs (licensing, subscription fees, maintenance costs, …) leading to higher higher overall expenses.
Elix features: Over 15 years of experience at your fingertips
Elix addresses these challenges head-on by integrating all core business functions into a single, user-friendly platform. It synchronizes your operations from ticketing to Agile Project Management and everything in between, ensuring that the left hand knows what the right hand is doing, and they’re both clapping in applause at how smooth everything runs.
Why choose Elix?
Elix is the top choice for private and public organizations seeking a secure and modular Business Management tool.
On-Premise Solution
Unlike other solutions, Elix provides secure on-premise deployment, giving you full control over your infrastructure and sensitive data
Complete & Modular
Built on microservices & Micro-frontend architecture, Elix lets you select the modules you need, without the heavy price tag and all-or-nothing plans.
Low Code Platform
Our low-code builder allows you to effortlessly create and manage objects, forms, workflows, APIs, and charts using a simple drag-and-drop interface.
Highly Customizable
Elix adapts to your organization’s unique workflows, ensuring that the system fits perfectly into your operational structure.
Optimized for different sectors
Elix is designed to be a versatile solution, meeting the diverse needs of various industries.
Say goodbye to business chaos and hello to streamlined success.
Book your free Elix demo today!
Why AI matters for public administration: 4 compelling reasons!

AI, widely acknowledged as a powerful tool to boost efficiency and productivity, has made remarkable success, gaining traction across various sectors and activities.
1. AI, a catalyst for E-Government Development
- In Australia, the Business Registration Service, equivalent to Tunisia’s National Business Register, uses an AI-powered chatbot to guide users through the business registration process, providing real-time assistance and reducing the reliance on administrative staff.
- In New Zealand, the Companies Office uses predictive models to identify potentially fraudulent business registrations, ensuring a safer investment environment.
2. AI, a vital ally during crises
This example demonstrates the crucial role AI plays in enabling governments to respond swiftly and effectively in situations of crisis.
3. AI, a resource optimization tool
For instance, Singapore has used AI to automate processes such as birth registration and elderly care through its Life SG service, providing faster and more accurate services to its citizens.
Similarly, in India, the “Saagu Baagu” pilot project in agriculture used AI to assist 7,000 chili farmers, significantly improving productivity, quality, and, consequently, farmers’ incomes.
4. AI supporting strategic planning
Conclusion: AI will be a cornerstone of future E-Governments
In conclusion, AI offers transformative opportunities for public administration by enhancing efficiency, improving service delivery, and enabling better resource management. Governments around the world are increasingly adopting AI to streamline processes, optimize operations, and respond effectively to crises.
The technology also plays a critical role in strategic planning, providing valuable insights for data-driven decision-making. As public institutions embrace AI, they are better equipped to meet the evolving needs of citizens and deliver responsive, modern governance enabling them to achieve higher levels of development and competitiveness. Ultimately, AI will be a cornerstone of future E-Governments, fostering innovation and sustainable public services.
Content
How IT projects succeed: Opportunities and limits of agile software development

A lot has changed in the IT world: Companies are increasingly focusing on digital transformation and modernisation, but despite these efforts, many projects still fail. Studies show that 70% of digital transformation projects do not fully achieve their goals. There are many reasons for this: from unclear alignment and a lack of prioritisation to outdated technologies and inadequate risk management. This also applies in particular to the implementation of IT projects.
As think tank, we can look back on many years of experience in the consulting and implementation of IT projects. We have experienced the developments in agile software development at first hand and have successfully implemented them in numerous projects. But agility is not always the best approach. Let us shed light on how agile methods can revolutionise IT projects – and where they reach their limits.
How agile methods can support the success of IT projects
Better alignment through continuous communication
Clear target definition and rapid measurement of success
Effective risk management and prioritisation
Where agile methods reach their limits
High regulatory requirements
Agility can be problematic in highly regulated sectors such as finance or healthcare. There are often strict legal requirements that demand clear documentation obligations and clearly defined processes. A classic waterfall model has proven to be advantageous here, as it enables precise planning and long-term documentation that fulfils regulatory requirements.
Complex dependencies and legacy systems
Lack of experience with agile methods
Our proven approach: The right method for your project
- How high is the degree of uncertainty or change?
High uncertainty requires agile methods, while more stable projects can benefit from classic models. - What resources and technologies are available?
We rely on agile or hybrid approaches for modern technologies and agile teams, and on more traditional methods for legacy systems. - How high are the requirements for control and documentation?
In highly regulated projects, we favour classic project management, while less regulated projects benefit from agile methods.
Conclusion: Choosing the right method leads to sustainable success
As an experienced consultancy, at think tank we combine agility where flexibility is required with traditional approaches when stability and control are needed. This hybrid approach has proven to be particularly successful in many projects.
Let’s find the best way for your IT project together – and make it a success.
Content:
think tank Research and Innovation Initiatives
for a better future
Research and innovation are crucial to finding new solutions to social, technological and environmental challenges. They not only promote economic growth, but also improve the quality of life and drive progress in science and technology. They also help to ensure competitiveness and support sustainable developments.
AILAC – focussed solution initiatives
Real research and development is only possible when ideas are dedicated and a strong commitment to long-term innovation initiatives and projects is shown.
We believe that it is the role of small companies to be a source of innovation and to develop solutions that go beyond the state of the art and are based on new and provocative thinking.
This is our definition of a think tank and the reason why we decided to set up our own AI lab, AILAC, in Tunis, where we develop ground-breaking solutions.

Steve Jobs
Strategic industry initiatives
We believe in collective intelligence, which is why we pursue strategic, long-term research and development initiatives together with our business partners and customers. The complexity of digital technologies requires the coming together of many minds to develop truly new, ground-breaking technologies and solutions. For this reason, we are pursuing multi-year initiatives focussing on AI and digital transformation technologies with major industry partners and, in some cases, with large cross-industry consortia:
- One of our key research projects involves the development of high-performance edge intelligence cameras. The use of such cameras is essential for automotive vehicles and machines. The camera takes over the evaluation of the image information through to scene recognition and provides decision information to the central model of the mobile unit or machine.
- Another innovation project focuses on intelligent agents that provide end-to-end support for design and development processes in the electronics and automotive industries. On the one hand, this relieves employees of the exponentially increasing design complexity and, on the other, greatly reduces errors or inefficiencies in the design and manufacturing process.
- A project looking further into the future is concerned with the integration of universal edge intelligence in semiconductor products. In-silicone intelligence will make it possible to make all digital products more efficient and effective throughout their entire life cycle or to extend the life cycle. The goal here is software-defined silicone products.

“As a pioneer of digital transformation, it is a matter of course for us to work with partners on research projects so that we are always at the cutting edge or ahead of the curve.”
Mohamed Chergui
CEO
think tank opens state-of-the-art data science and AI lab in Tunis

Munich, 05 September 2024. think tank Business Solutions, an expert in digital transformation and innovative technologies, is once again taking the path of innovation and opening its own AI and data science laboratory, AILAC, to take a leading role in this field.
Establishing a lab and not just a competence center lays the foundation for future leadership in the domain and is a response to think tank’s customers increasing deep-collaboration demand.
The Tunis location underlines the strategic AI growth potential think tank sees in Africa.
With AILAC think tank answers the changing market reality. African customers are increasingly becoming “made in Africa” sensitive. Change aspects and specific customization, knowledge transfer and joint research and innovation projects require local affinity and Tunis with a 2.5 million population and excellent university clusters is the gateway to Africa.
Of course, AILAC will also service European markets and in particular the French and DACH markets through its offices in Munich and Zurich and their consulting partners in Europe. In this way, think tank takes into account the different market need, the highly dynamic explorative and experimental African markets as well as the mature and regulated European market. AILAC stands for “AI Out of Africa” and considers the specific needs of customers on a continent six times the size of the EU, with completely different prerequisites and development contexts.
“As artificial intelligence evolves from exotic use cases to E2E processes, and from megawatt data centers to edge intelligence in the tiniest of objects so does our clients’ demand for real business intelligence In Europe we see a strong trend towards joint research and innovation projects with our customers and of course AI Strategy and Governance are key topics and concerns, while African customers want to reap the benefits of being leap-scale adopters with many more degrees of freedom,” says Alexander Vocelka, Senior AI Advisor at think tank.
“AILAC will develop completely new data science methods and machine learning models and work on cybernetic concepts as well as support the delivery of state-of-the-art business solutions,” explains Mohamed Guermazi, Head of AILAC in Tunis.
“Digital transformation without intelligization will be impossible in the future. think tank’s future expansion will be strongly driven by artificial intelligence solutions and with AILAC we set the course accordingly. AILAC is probably the most exciting step into the future for think tank since its foundation and we are very excited to release some of our new solutions as soon as this fall,” explains Mohamed Chergui, founder and CEO of think tank.
AILAC products will range from intelligent business platforms and next generation digital assistants to complete industry specific business optimizers for SMEs. Research is being conducted in the area of maximum edge intelligence in remote objects and off-line machines as well as micro-sensors of all types.
About think tank
think tank Business Solutions is a medium-sized company based in Munich with branches in Tunisia and Switzerland. The company has been offering business and IT consulting as well as innovative customised software solutions for the automotive, manufacturing and financial sectors for decades. As an expert in digital transformation and innovative technologies, think tank Business Solutions AG also supports customers on their path to agile transformation. Another focus of its business activities is information security. In the coming years, the company will also increasingly focus on artificial intelligence in its solutions.
Marketing & Communication Team
Dorothee Schwarz
+49 (0)89 552677-0
Sarah Cherif
+216 71 784 726
Risk Management and Compliance:

By implementing effective risk management, companies can make their business processes more secure and resilient. Risk management is the targeted analysis and treatment of risks and dangers that threaten companies. It encompasses all activities, decisions and measures to minimise the probability of occurrence or the potential damage of risks. It is a systematic approach to identifying, assessing and managing potential risks.
Objectives and tasks in risk management
The tasks of a risk management system include the identification and assessment of various types of risks, such as market, default or compliance risks. The primary objective is to create robust operational processes, e.g. to avoid financial losses and protect physical and human resources. Other tasks include risk monitoring and control as well as the provision of risk information for strategic decisions. A well-implemented risk management system enables companies to react proactively to risks and thus be successful in the long term.
Importance of risk management for companies
Benefits of risk management for companies
The main task of risk management is to safeguard the company’s existence and minimise unforeseen events. However, it also helps to create a better basis for business decisions by analysing the effects of options for action as well as to create transparency regarding planning reliability and reduce deviations from the plan. Systematic risk management enables companies to improve their competitiveness and increase their resilience
Legal significance of risk management and compliance risks
In Germany, the requirements for risk management e.g. are characterised by the German Law on Control and Transparency in Business (KonTraG) and the IDW standard for auditing the early risk identification system in accordance with Section 317 (4) of the German Commercial Code (HGB) (IDW PS 340). These require the systematic and regular identification and quantification of risks (ISO-31000). All companies are required to implement an appropriate risk management system in order to ensure the continued existence of the company and minimise liability risks.
Risk analysis and assessment
Risk analysis & risk monitoring
Sub-tasks of risk management are risk analysis, risk management and the preparation of risk information for business decisions, such as investment valuations. Below you will find an overview of the most important steps:
1. Preparation
Objectives and scope definition
- Define objectives: Determine the specific objectives of the risk analysis, e.g. protecting sensitive data or ensuring the availability of critical systems.
- Define scope: Define the scope of the analysis by specifying which information, systems, processes and organisational units are to be considered
Team composition for initiation
- Risk management team: Form a team of e.g. experts from the areas of: Information Security, IT, Legal and Business to incorporate different perspectives and expertise when implementing risk management.
- Select methodology: Decide on a suitable methodology for risk analysis, such as ISO/IEC 27005, NIST SP 800-30 or another proven approach.
- Documentation: Prepare templates and documentation tools to record the results of the risk analysis in a structured manner.
2. Risk identifikation
Collection of information
- Asset identification: Create a list of all relevant information assets, such as data, hardware, software, networks and employees.
- Threats and vulnerabilities: Identify potential threats (e.g. cyberattacks, natural disasters, historical data) and vulnerabilities (e.g. outdated software, untrained employees) that could jeopardise information assets.
Interviews and workshops
- Stakeholder involvement: Conduct interviews and workshops (e.g. SWOT analysis) with relevant stakeholders to gather additional information on threats, vulnerabilities and existing security measures.
3. Risk assessmant
Risk analysis (qualitative and quantitative analysis)
- Probability of occurrence: Evaluate the probability with which a threat could exploit a vulnerability.
- Impact: Determine the potential impact of a successful attack or incident on information assets and the organisation.
Risk matrix
- Create a risk matrix: Present the results of the risk analysis in a risk matrix to categorise the risks according to probability of occurrence and impact.
- Prioritisation: Prioritise the identified risks to identify those with the highest urgency and the most serious impact.
4. Risk management
Action planning
- Define measures: Develop suitable risk management measures, such as risk avoidance, risk minimisation, risk transfer or risk acceptance.
- Implementation plan: Create a detailed plan for implementing the defined measures, including responsibilities, resources and time frame.
5. Risk monitoring and review
Continuous monitoring
- Monitoring: Implement mechanisms to continuously monitor the risks and the effectiveness of the measures taken.
- Reporting: Establish regular reports and reviews to track the status of risks and measures.
Review and adaptations
- Periodic review: Regularly review the risk analysis and adapt it to changing conditions or new threats and vulnerabilities.
- Lessons learnt: Gather experience from incidents and adjustments in order to continuously improve risk management.
6. Documentation and communckation
Documentation
- Record the results: Document all steps of the risk analysis, including the identified risks, the assessment results and the planned measures.
- ISMS documentation: Integrate the risk analysis into the overarching ISMS documentation in order to create a consistent and comprehensible information basis.
Communication
- Inform stakeholders: Communicate the results of the risk analysis and the planned measures to all relevant stakeholders, risk owners, affected departments and management.
- Raise awareness: Promote awareness of information security and the importance of risk management within the organisation.
Differentiation between compliance and risk management
While risk management serves to manage potential risks, compliance management aims to ensure compliance with legal, contractual and other regulatory obligations. Risk management proactively identifies and manages risks, compliance management ensures that the company acts in accordance with the rules. Both disciplines complement each other and together contribute to the stability and sustainability of the company.
Synergies between risk management compliance
Established risk management is essential in order to effectively manage market, default and compliance risks. By identifying, assessing and managing risks, corporate goals can be better achieved. Optimising the interaction between risk management and compliance can also achieve synergy effects. The integration of both systems in the ISMS enables a transparent view. This leads to better decision-making and ultimately to sustainable business success.
The future of risk management and compliance
The future of risk management will be characterised by technological innovations, the increasing complexity of global markets and changing regulatory requirements. There are a number of trends and developments that could shape risk management in the future:
1. Digitalisation and technological innovations
- Automated risk identification: AI and machine learning enable the automatic detection of patterns and anomalies that could indicate potential risks.
- Predictive analytics: The use of predictive analytics enables risks to be recognised at an early stage and preventive measures to be taken.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies
- Transparency and traceability: Blockchain technologies can improve the transparency and traceability of transactions and data flows, which is particularly beneficial in financial and supply chain management.
- Security improvements: The immutable nature of blockchain can help ensure the integrity of data and prevent tampering.
2. Sustainability and ESG risks (environmental, social, governance)
- ESG integration: Companies will increasingly integrate environmental, social and governance risks into their risk management processes to ensure long-term sustainability and compliance.
- Sustainability reporting: Transparent reporting on ESG risks and measures will become increasingly important and will be demanded by investors and regulators.
3. Regulatory developments and compliance
Stricter regulations
- Data protection and cybersecurity: Regulations such as the EU GDPR and the Cybersecurity Act require companies to implement comprehensive measures to protect personal data and cybersecurity.
- Financial regulation: International regulations such as Basel III and Solvency II are further tightening risk management requirements in the financial sector.
Global standards and frameworks
- ISO standards: The importance of international standards such as ISO 31000 (risk management) and ISO 27001 (information security management) will continue to grow.
- Best practices: Companies will increasingly rely on best practices and frameworks to improve their risk management systems.
4. Crisis management and resilience
Proactive risk management
- Crisis plans and simulations: Companies will increasingly develop crisis plans and carry out regular crisis simulations in order to be prepared for unexpected events.
- Business Continuity Management (BCM): The implementation of BCM processes will ensure that critical business processes can be maintained even in crisis situations.
Increasing resilience
- Resilience: The ability of a company to recover quickly from disruptions and adapt to change is becoming a central component of risk management.
- Flexible structures: Flexible organisational structures and adaptive business models will help to increase resilience to external shocks.
Conclusion: Cooperation between risk management and compliance is crucial
Companies can only be prepared for future challenges if risk management and compliance work closely together. A holistic approach in both areas can minimise risks and prevent damage to the company. A well-functioning and established information security management system is a good basis for successful risk management.
Content:
Improve data quality: Top 7 strategies for better results

Improving data quality is essential for making well-founded business decisions. In this article, you will learn specific strategies for systematically increasing data quality and maintaining it at a high level in the long term.
Das Wichtigste auf einen Blick
- A common understanding of business terms within the company is essential.
- A continuous process of data quality management, including regular measurement and a robust data quality management framework, is crucial to ensure high data quality in the long term.
- Technological solutions such as data cleansing tools and monitoring tools help to maintain data quality, while training sensitises employees to the importance of data quality and enables them to actively contribute to quality assurance.
Definition and importance of data quality
Data quality is crucial to the success of a company. It refers to the quality, accuracy and usefulness of data for its intended purposes. Think of data as the foundation on which your organisation is built. If this foundation is fragile, any decision or strategy based on it will be unstable. If there is no solid data management in place, the data collected can be worthless. As a result, the full potential is not realised. So it’s not just about having data, it’s about having the right data in the right quality at the right time.
A common understanding of data is essential to ensure that all areas of the company understand what certain business terms or data objects mean and what they do not. Only if all departments start from the same definitions and quality standards can a company truly be data-driven and realise its full potential.
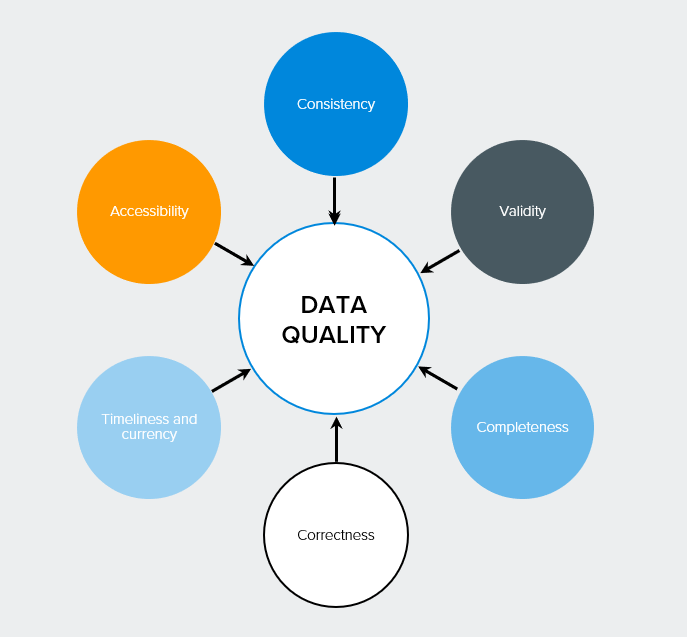
Strategies for improving data quality
Improving data quality is not a one-off process, but a continuous process that requires strategic thinking and consistent action. Data quality should be understood as a continuous process, often described as a “closed-loop” or “data quality circle”. This approach ensures that the quality of your data is not only improved, but also maintained at a high level in the long term.
A structured approach to data quality management is the key to high data quality as a repetitive and flexibly adaptable process. This means that you not only react reactively to problems, but also take proactive measures to continuously improve the quality of your data. It is recommended that you select a pilot area to start with so that you can easily integrate data quality management into your day-to-day business. This will allow you to gain experience and refine your strategy before rolling it out across the organisation.
The involvement of stakeholders and consultants is another critical success factor. It helps to avoid misunderstandings and make changes in business processes transparent. By involving all relevant parties from the outset, you ensure that your data quality initiatives are widely supported and can be implemented effectively.
In the following sections, we will look at some specific strategies that will help you to improve your data quality in the long term.
Continuous measurement of data quality
Continuously measuring data quality is the compass that navigates your organisation through the sea of data. Understanding the issues and recognising their impact is critical to improving data quality. Without regular and systematic measurement, you will be in the dark and unable to respond effectively to problems or track improvements.
An audit to determine the status quo can be a useful starting point. Building on this, you should implement an automated process. The regular review and adjustment of data quality requirements is necessary to fulfil current needs. Remember: you can’t improve what you can’t measure. By defining clear metrics and targets for your data quality and reviewing them regularly, you create the basis for continuous improvement and can demonstrate the success of your efforts.
Establishment of a data quality management framework
A robust data quality management framework is the backbone of any successful data quality strategy. Data quality management comprises three main elements: Data Profiling, Data Cleansing and Data Management. Together, these elements form a holistic system that ensures the quality of your data from collection to utilisation.
Data profiling is a fundamental method for analysing the quality of data and enables the identification of problems such as inconsistencies, missing values and discrepancies within data sources. By using data profiling tools, you can gain a clear picture of the state of your data and initiate targeted improvement measures. The regular verification and updating of address details is a practical example of how you can improve data consistency.
By implementing a structured framework that covers all these aspects, you create the conditions for a sustainable improvement in your data quality.
Training and sensitisation of employees
The best technologies and processes are only as good as the people who use them. Training employees in the handling of data and its quality is effective in practice because, in addition to technical support, it provides employees with enormous assistance in their daily work. By sensitising your employees to the importance of data quality and providing them with the necessary skills, you create a culture of data excellence in your company.
It is important that teams are always up to date to ensure that they do not slack off and continuously improve data quality. Regular training, workshops and best-practice sharing can help to ensure that the topic of data quality remains firmly anchored in the minds of all employees. Remember: every employee who works with data is a potential data custodian.
By empowering and motivating everyone involved to contribute to data quality, you create a strong foundation for long-term success.
Technological solutions to support data quality
In today’s digital era, technological solutions play a crucial role in improving and maintaining data quality. To ensure the accuracy and completeness of data, the implementation of data cleansing and data validation tools is a common method. These tools are used to cleanse data and check its accuracy. These tools act as digital guardians that work tirelessly to keep your data clean and reliable.
In addition, data integration tools can help ensure that data from different systems and processes is consistent and standardised to improve analysis. Think of these tools as digital translators that ensure all your data sources speak the same language. This is especially important in large organisations with many different systems and departments.
besonders wichtig in großen Unternehmen mit vielen verschiedenen Systemen und Abteilungen.
It is important to note that real-time analyses and artificial intelligence require a stable database to function smoothly. Without high-quality data, even the most advanced AI systems will not be able to deliver reliable results. By investing in technological solutions to improve data quality, you are laying the foundation for future innovation and data-driven decision-making in your organisation, including business intelligence.
Use of data cleansing tools
Data cleansing tools are the Swiss army knives in your data quality toolkit. Data cleansing is the process of detecting and correcting errors and inconsistencies in data, including identifying and removing duplicates, incorrect values and inconsistent information. These tools work tirelessly to clean and optimise your data sets so that you can focus on analysing and using the data.
There are a variety of data cleansing tools on the market, each with its own strengths. Here are a few examples:
- OpenRefine: A popular open source tool for data cleansing that can convert data between different formats.
- Trifacta Wrangler: Uses machine learning to suggest data transformations and aggregations, which speeds up and simplifies the cleansing process.
- Melissa Clean Suite: Improves data quality in CRM and ERP platforms with functions such as data deduplication and data enrichment.
The choice of the right tool depends on your specific requirements and the complexity of your data landscape.

Integration and harmonization of data
In today’s networked business world, the integration and harmonisation of data from different sources is essential for a holistic view of your company. A unified analytics platform can ensure a consistent view of all company data in a kind of digital control centre where all your data streams converge and interact harmoniously with each other.
The introduction of a central hub, linked to relevant systems, can act as a single point of truth and automates data checking during input. This ensures that your integrated data is not only merged but also continuously checked for quality.
Monitoring tools for monitoring data quality
Continuous monitoring of data quality is like an early warning system for your data management. Automated tools for the continuous monitoring of data quality can detect inconsistencies, redundancies and missing data and report them via automated alerts if necessary. This enables you to react proactively to problems before they develop into major challenges.
Modern data quality tools make this possible:
- the connection and reading of source systems via APIs
- the efficient checking and cleansing of data
- Live tracking of the status of the data quality
- the creation of reports
This can take the form of a real-time dashboard for your data quality, which gives you an overview of the health of your data at all times. Data monitoring is used to monitor the status of the data. This status is then documented in a comprehensible manner.
Regular reviews and audits help to recognise and rectify data problems at an early stage. By using such tools, you create a culture of continuous improvement and vigilance with regard to your data quality.
Practical measures to avoid data quality problems
Now that we have looked at strategies and technological solutions, it is time to look at concrete practical measures that can prevent data quality problems from occurring in the first place.
Introducing a centralised hub, connected to relevant systems, can act as a single point of truth and automate data checking as it is entered. This ensures that your integrated data is not only merged, but also continuously checked for quality.
The following measures are important for improving manual data entry:
- Check for plausibility and form
- Verification of address details
- Input validation using reference values
- Duplicate search
These measures form the first line of defence against data quality problems.
One problem that is often overlooked is data silos, which often arise due to organisational structures that promote the separation of data in different departments. The data silos of individual departments often lead to inconsistent and inaccurate analysis results. It is important that organisations integrate their data to achieve accurate and consistent results. To combat this problem, it is important to develop an organisation-wide data strategy that transcends departmental boundaries and provides a unified view of company data.
In the following sections we will look at some specific approaches to implementing these practical measures using a guideline.
First-Time-Right approach
The first-time-right approach is like the “measure twice, cut once” principle in the world of data. The ‘first time right’ principle in data management aims to avoid incorrect or incomplete data as soon as it is captured. This means that you focus on quality right from the start and thus minimise the effort required for subsequent corrections.
Shortcomings in manual data entry can be reduced by measures such as intelligent input masks and input validations. These can perform plausibility and form checks during data entry. A practical way to implement the ‘first time right’ approach is to use user-friendly front-ends such as Microsoft Excel for data entry. By providing intuitive and error-resistant input interfaces, you make it easier for your employees to capture high-quality data right from the start.
Remember: Every error prevented during data entry is a step towards better data quality and more efficient processes, which can also reduce costs. You can optimise this process even further with our tips.
Avoidance of data silos
Data silos are like isolated islands in your sea of data – they hinder the free flow of information and lead to inconsistent and incomplete views of your organisation. A strong corporate culture that encourages data sharing is crucial to prevent data silos from forming. It’s about creating a mindset where data is seen as a shared resource that benefits all departments.
Data silos should be broken down and integrated on a standardised analysis platform to ensure a consistent view of all company data. A centralised data warehouse can help avoid data silos by integrating data from different departments and making it accessible. Think of a data warehouse as a kind of digital library where all your company data is catalogued, organised and accessible to any authorised user.
The regular synchronisation of data between departments also supports data consistency and helps to identify and rectify discrepancies at an early stage.
Regular data quality checks
Regular data quality checks are like regular health checks for your data. Integrating data quality checks into daily business processes helps to identify problems at an early stage. Instead of viewing data quality as a separate task, it should be an integral part of your daily business processes. This enables continuous monitoring and rapid response to potential problems.
Regular data quality checks can help to identify and rectify long-term data problems before they have a major impact. Integration into business processes is necessary to eliminate long-term identified data quality deficiencies. Remember that data quality is not a one-off project, but an ongoing process. By carrying out regular checks and incorporating the results into your business processes, you create a cycle of continuous improvement that constantly increases the quality of your data.
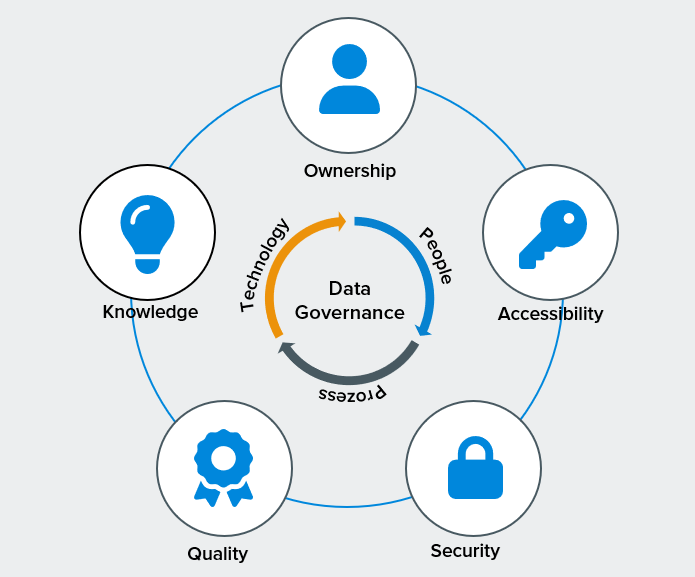
Data governance as the key to long-term data quality
Data governance is the foundation on which long-term data quality is built. It is like a set of rules that ensures that data is managed consistently, reliably and securely. Organisations should establish clear responsibilities in a top-down approach to raise awareness of data quality at all levels. This means that the initiative for data quality must come from the management level and be carried through all levels of the organisation.
Data governance requires the distribution of responsibilities for data creation, maintenance and quality assurance, whereby data owners require decision-making competences. Data owners require decision-making authority and are supported by the technical expertise of the data stewards. This distribution of roles ensures that there are clear contact persons and persons responsible for every aspect of data management.
One goal of data governance is to find an optimal combination of preventive and reactive measures for the early detection of data problems. This means that you not only react to problems, but also take proactive measures to prevent data quality issues before they arise.
Summary
In this comprehensive guide, we have highlighted the critical importance of data quality to business success. From the definition and importance of data quality to practical strategies for improvement, technology solutions and data governance, we have covered all the key aspects of effective data quality management. We learnt that data quality is not a one-off project, but a continuous process that needs to be integrated into daily business operations.
Implementing robust data quality management may seem like a challenge at first, but the potential benefits are immense. Improved decision making, increased efficiency, cost savings and a competitive advantage are just some of the rewards you can reap. Remember, in today’s data-driven world, quality data is not just an advantage, it’s a necessity. By implementing the strategies and best practices outlined in this guide, you’ll lay the foundation for a future where your data is not just a resource, but a true asset to your organisation. Make data quality your top priority and you will reap the rewards in the form of better business results and a sustainable competitive advantage.
Frequently asked questions
What are the most common causes of poor data quality?
The most common causes of poor data quality are manual input errors, outdated data, data silos, a lack of standardisation and insufficient data validation. A lack of employee training and the absence of clear data governance guidelines can also lead to quality problems. It is important to identify these causes and take appropriate measures to improve data quality.
How can I measure the ROI of investments in data quality?
You can measure the ROI of investments in data quality by looking at factors such as reduced error rates, improved decision making, increased productivity and cost savings. Improvements in customer satisfaction and sales can also be indirect indicators of ROI.
What role does artificial intelligence play in improving data quality?
Artificial intelligence plays an important role in improving data quality by using it for automated data cleansing, anomaly detection and predictive analyses. AI algorithms can uncover hard-to-recognise patterns and inconsistencies, improving the efficiency and accuracy of data quality processes.
How can I sensitise my employees to the topic of data quality?
To sensitise your employees to the topic of data quality, you can conduct regular training sessions, workshops and internal communication campaigns. Show concrete examples of the effects of poor data quality and establish a culture of data responsibility. Reward employees who are committed to improving data quality.
How often should data quality checks be carried out?
Data quality checks should be performed at different frequencies depending on the type and use of the data. Critical business data should ideally be monitored continuously, while less critical data may be reviewed weekly or monthly. It is advisable to implement automated checks and perform regular manual audits to avoid problems.
Inhalt:
Mastering test automation in software development

In today’s software development, short development cycles are a prerequisite for meeting the demands of the market. Test automation is therefore essential to ensure the quality of the software in the long term. With automated tests, companies can develop faster and at the same time ensure higher software quality. As a result, savings of up to 30 and 90% respectively can be achieved in both test costs and test time. In addition, a return on investment (ROI) of up to 100% is possible within two years of test automation.
Advantages of test automation
The introduction of test automation has many advantages:
- Savings of up to 30-50% of test costs
- Return on investment (ROI): ROI of up to 100% within the first two years after the introduction of test automation.
- Reduction of test time by up to 90%, especially for recurring regression tests
- Quality assurance
- More frequent releases: shortening release cycles from months to weeks or even days
- Accelerated further development: through faster feedback to developers and the associated bug fixing.
- High level of standardisation through defined, proven processes and responsibilities
- Flexibility through short iterations and retros
- Clear communication and status reports
- Transparency of processes and those responsible
- Performance measurement thanks to reports
Challenges of test automation
The challenges of test automation are manifold and require careful planning and execution. One fundamental challenge is to build up the expertise of employees so that they can effectively develop and maintain automated test cases. No less important is defining the right test cases. Here, it is often more realistic to aim for 70% coverage of functionalities rather than pushing for full coverage, which is often neither practical nor cost-effective. In addition, the adaptation and maintenance of test cases requires continuous attention in order to keep pace with changes in the software applications.
The integration of the test team into the development process and the early planning of new features into the test concept are also crucial. This includes considering the impact of new features on existing test cases, which increases complexity and requires a well-thought-out test strategy and precise test planning.
Other critical aspects are the quality and maintainability of the test data and the test artefacts themselves. Guaranteeing valid test data for every scenario and ensuring a consistent structure and utilisation of the test libraries are essential for effective test runs. High maintenance efforts,
especially the editing and customisation of test scripts, are often challenging. Artificial intelligence (AI) can offer a solution here by supporting automated processes for the maintenance and optimisation of test cases, which can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of test automation overall.
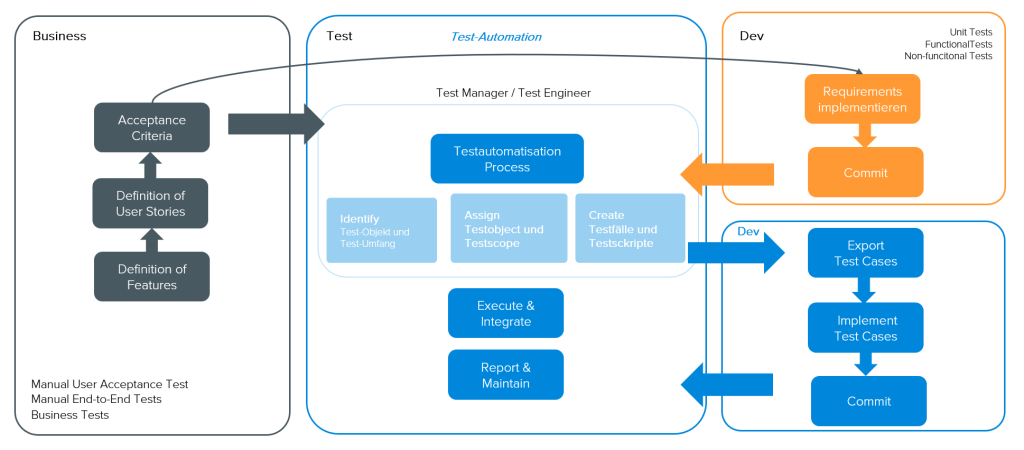
Integration test automation
In order to meet these challenges, precise planning of the automation of tests for the development of a product is necessary. It is helpful to bundle the activities and roles in a test hub with the following steps:
1. Discovery Phase
The goals of the discovery phase are:
- Understanding the context, challenges and needs: Only with a full understanding of the specific context of the project can customised solutions be developed that cover the actual needs.
- Recognising and minimising risks: By proactively analysing risks negative impacts on the project can be avoided and a stable basis for development can be created.
- Holistic illumination of the project environment: A comprehensive illumination of the project environment with regard to both technical and organisational processes ensures a comprehensive understanding of the project landscape.
- Make the start of development as simple as possible: Clear processes, easy-to-understand instructions and a well-prepared infrastructure make it easier for everyone involved to get started.
2. Managing and planning
Issues such as the right test automation tools, definition of roles and responsibilities and the use of an appropriate test architecture must be clarified in advance.
Only then can the actual planning and control begin. The following aspects need to be considered during planning:
Development of automation strategies
Ensuring seamless integration of the tests in the build pipeline
Creation of a test concept
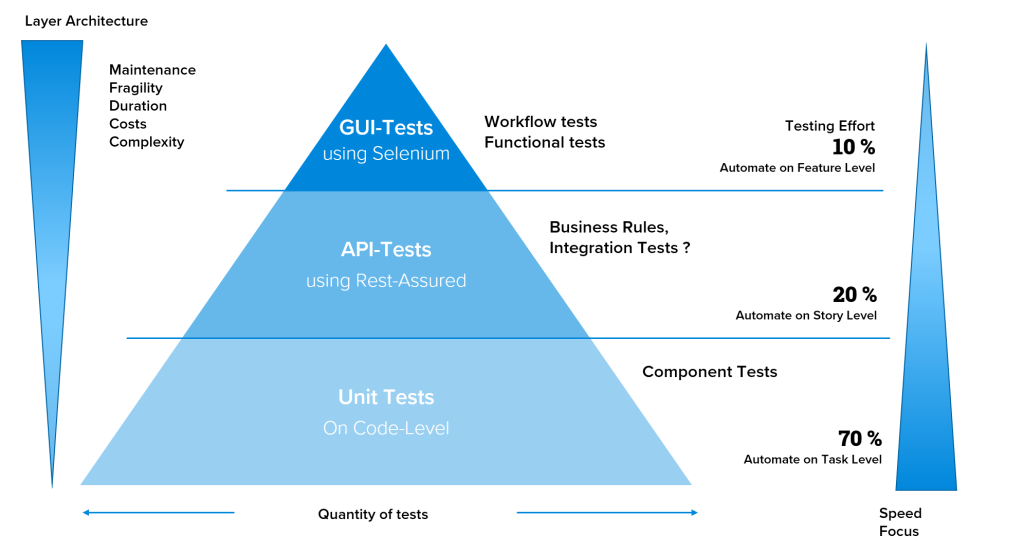
Specification of tests, taking into account the layer architecture (test pyramid)
The diagram shows that the costs, complexity, maintenance effort, duration/performance and fragility for GUI tests are far higher than for unit or API tests. Therefore, a sensible distribution taking into account the criteria mentioned above is absolutely essential:
- Layered architecture makes it possible to define test-specific layers that cover different aspects of the system
- Lowest level: Unit tests that test individual code sections and functions. By finding errors early on in this phase, problems can be rectified cost-effectively before they affect higher layers.
- Middle level: API tests that test the interfaces between the various components. Here it is checked whether the data is sent to the server and processed correctly, which ensures the integrity of the communication paths.
Requirements for test automation tools
- Ease of use of the tools, as this makes it easier to get started and shortens the learning curve for the test team.
- Comprehensive log output for detailed logging to analyse the test results in order to draw conclusions about the quality of the tested system.
- Recording of user tests to simplify the creation of test scenarios by recording user actions.
- Recording of test scripts and test activities for the systematic and repeatable execution of software tests.
- Recording of test execution through screenshots or videos for visual documentation of process steps.
- Simple programming language or low-code options to make it easier for less experienced team members to create and maintain the tests, thereby increasing the productivity of the team.
- Parameterisation to keep maintenance efforts low and achieve greater flexibility in the execution of test scripts
Roles and responsibilities
- The test manager is responsible for the test concept. He ensures that the software meets the quality standards and fulfils all requirements.
- The test engineer is responsible for defining the test cases and executing the test cycles as well as analysing the test reports
3. Project phase: realisation and implementation
In the project phase, the infrastructure and the tool chain are set up on the basis of the analyses and definitions carried out in the previous phases.
Piloting and stabilisation as part of a proof of concept (PoC) is also useful.
The implementation of a critical workflow (standard use case) is crucial in order to gain initial experience, avoid errors and be able to react quickly. It is equally important to adapt and create an operating manual and technical documentation.
Comprehensive training of all project members is essential to enable the test team to implement automated tests quickly. Training and know-how transfer sessions are crucial elements in enabling the test team to act quickly.
Test automation with artificial intelligence
In order to fully utilise the benefits of test automation, the use of AI is essential. AI offers numerous support approaches for carrying out test automation in a cost- and resource-efficient manner. It can support the following tasks, among others:
- Creation of test cases (guided test case design)
- Determination of test coverage
- Creation & implementation of the Gherkin tests
- Visualisation of test cases (test-based modelling)
- Determination of standard case deviation (GUI test)
- Analysing errors (classification)
Conclusion
Test automation is particularly important for long-term and medium-sized to large software development projects. With well thought-out structuring and planning, it offers numerous advantages: it speeds up the development process, reduces costs and significantly improves the quality of the software. However, successful test automation requires careful planning, a comprehensive test concept and the use of modern test tools and technologies.
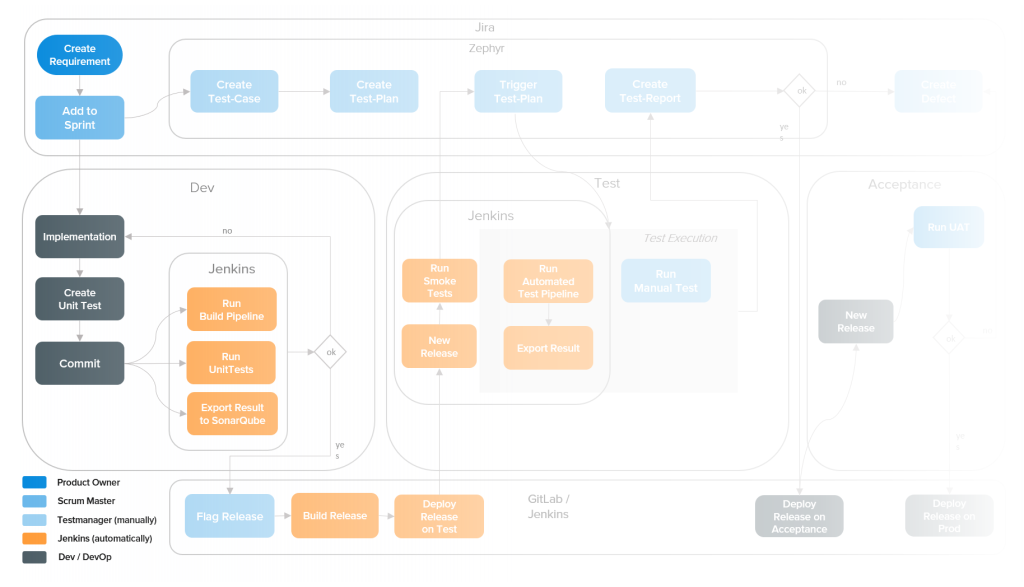
Blue Print für your Test Automation
Easily integrate and implement test automation. How can you do this? Find out more in our e-paper!